Web模拟器:y86-64 Simulator
项目源代码:Invisiphantom/Y86-64-Single-Cycle
项目环境配置:IVerilog+VSCode环境配置 | Mind City
项目代码解析:Y86-64单周期CPU设计 | Mind City
- 相关项目
- RISC-V单周期CPU:RISC-V单周期CPU设计 | Mind City
- RISC-V流水线CPU:Invisiphantom/RISC-V-Pipeline
整体架构图(csapp P460)

- PC: 选择PCaddress的更新方式(累加or跳转)
- InstMemory: 从内存中取出PCaddress地址处的指令,并将其解析为对应的icode, ifun, rA, rB, valC
- PCIncre: 计算出下一条指令所在的内存地址valP
- Regs: 选择需要读取的寄存器和要写入的寄存器
- ALU_fun: 选择ALU需要执行的运算
- ALU_A: 选择ALU的数据A
- ALU_B: 选择ALU的数据B
- ALU: 执行运算并更新标志位
- CC: 根据标志位判断是否执行jXX或者cmovXX
- MemControl: 判断是否需要读写内存
- MemAddr: 选择读写内存的地址
- MemData: 选择写入内存的数据
- Mem: 执行内存的读写操作
- Stat: 判断CPU是否出现运行时异常
Y86-64指令集(Y86-64 Reference)
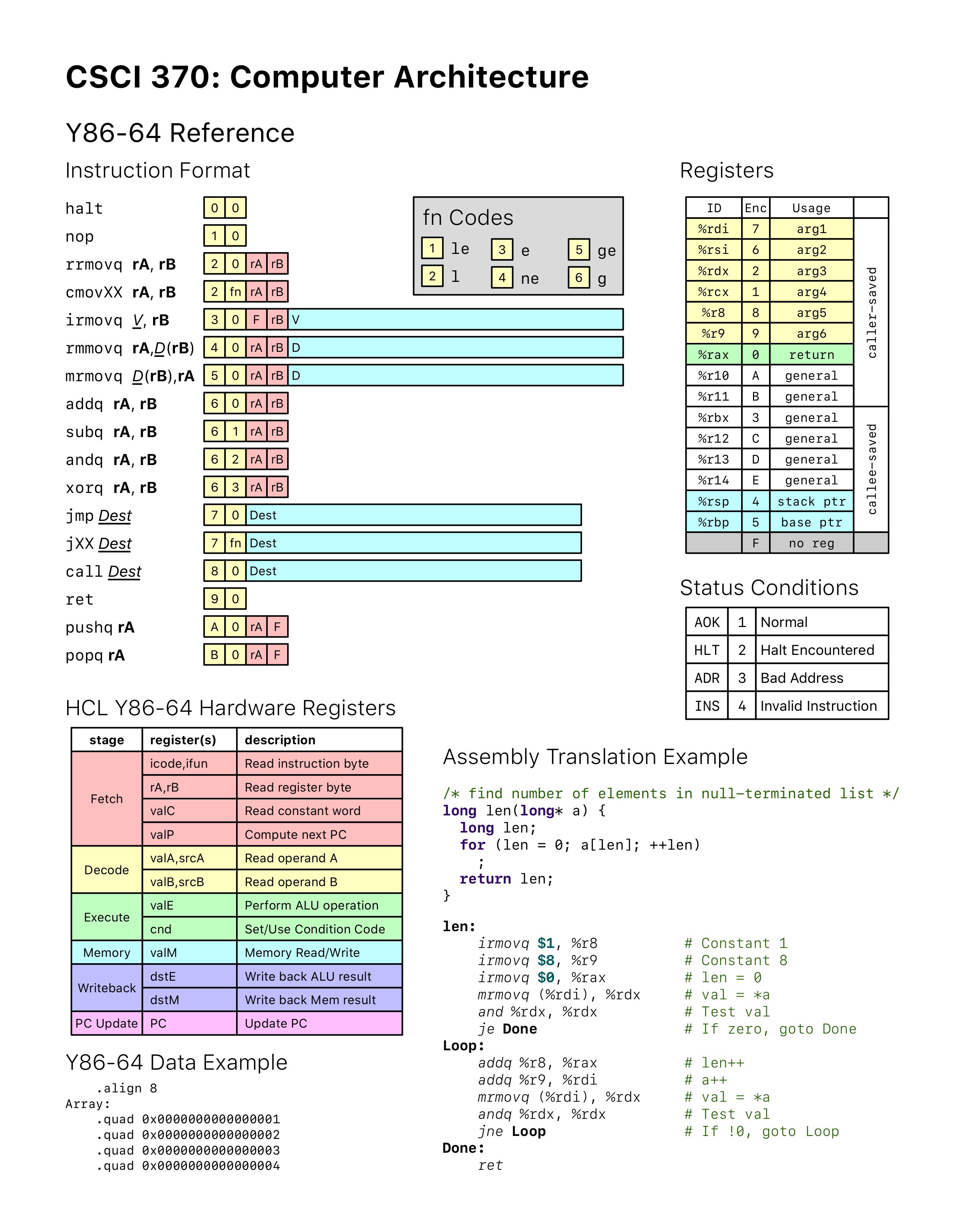
1 | Decode | Execute | Memory | Writeback |
- 2 rrmovq 需要读取rA寄存器 需要计算rA+0 不需要读写内存 需要写回rB寄存器
- 3 irmovq 不需要读取寄存器 需要计算valC+0 不需要读写内存 需要写回rB寄存器
- 4 rmmovq 需要读取rA和rB寄存器 需要计算rB+valC 需要将rA寄存器的值写入(rB+valC)地址的内存处 不需要写回寄存器
- 5 mrmovq 需要读取rB寄存器 需要计算rB+valC 需要读取(rB+valC)地址处的内存值 需要写回rA寄存器
- 6 ops 需要读取rA和rB寄存器 需要计算rB+-&^rA 不需要读写内存 需要写回rB寄存器
- 7 jXX
- 8 call 需要读取rRsp寄存器的值 需要计算rRsp-8 需要将valP写入(rRsp-8)地址处的内存 写回rRsp寄存器
- 9 ret 需要读取rRsp寄存器的值 需要计算rRsp+8 需要读取(rRsp)地址处的内存 写回rRsp寄存器
- A pushq 需要读取rA和rRsp寄存器的值 需要计算rRsp-8 需要将rA写入(rRsp-8)地址处的内存 需要写回rRsp寄存器
- B popq 需要读取rRsp寄存器的值 需要计算rRsp+8 需要读取(rRsp)地址处的内存 写回rA和rRsp寄存器
1 | ALU flags |
- ZF 零标志位 当ALU计算结果为0时置为1 否则置为0
- SF 符号标志位 当ALU计算结果为负数时置为1 否则置为0
- OF 溢出标志位 如果是加法,则当B和A同号且B和valE异号时置为1 否则置为0 | 如果是减法,则当B和A异号且B和valE异号时置为1 否则置为0
1 | fn Codes |
Verilog代码细节
PC
选择PCaddress的更新方式
- 默认更新为下一条指令的地址处
- jXX需要根据条件码来判断是否跳转到valC
- call直接跳转到valC地址处
- ret跳转到外层函数栈帧地址处
1 | module PC ( |
InstMemory
从内存中取出PCaddress地址处的指令,并将其解析为对应的icode, ifun, rA, rB, valC
1 | module InstMemory ( |
PCIncre
计算出下一条指令所在的内存地址valP
1 | module PCIncre ( |
Regs
选择需要读取的寄存器和要写入的寄存器
1 | module Regs ( |
ALU_fun
选择ALU需要执行的运算
1 | module ALU_fun ( |
ALU_A
选择ALU的A端的输入数据
1 | module ALU_A ( |
ALU_B
选择ALU的B端的输入数据
1 | module ALU_B ( |
ALU
执行运算并更新标志位
1 | module ALU ( |
CC
根据标志位判断是否执行jXX或者cmovXX
1 | module CC ( |
MemControl
判断是否需要读写内存
1 | module MemControl ( |
MemAddr
选择读写内存的地址
1 | module MemAddr ( |
MemData
选择需要写入内存的数据
1 | module MemData ( |
Mem
执行内存的读写操作
1 | module Mem ( |
Stat
判断CPU是否出现运行时异常
- AOK: 正常运行
- HLT: 执行HLT指令
- ADR: 访问非法地址
- INS: 读取非法指令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18module Stat (
input [3:0] icode, // HLT
input instr_valid,
input imem_error,
input dmem_error,
output reg [2:0] stat // 1: AOK, 2: HLT, 3: ADR, 4: INS
);
initial stat = 3'b001;
always @(icode or dmem_error) begin
#1; // 延迟写入使得output能与测试答案匹配
if (stat == 3'h1) begin
if (icode == 4'h0) stat <= 3'h2; // HLT
else if (dmem_error == 1'b1) stat <= 3'h3; // ADR
else if (instr_valid == 1'b0) stat <= 3'h4; // INS
else stat <= stat; // AOK
end
end
endmodule
arch
Y86-64单周期CPU顶层模块
- arch_tb: 顶层模块的测试模块
1 | module arch ( |
使用Python脚本批量测试Y86程序
运行代码前请先配置好WSL和IVerilog环境
脚本使用方式:打开Y86-Setup.py文件,使用Ctrl+Alt+N快速执行代码,如果测试输出与答案完全匹配,则终端输出All tests passed!
Y86-Setup.py顶层脚本整体功能:
清空
Y86-output文件夹使用
ROMpath.py将InstMemory.v和Mem.v中的$readmemh()路径替换为当前目录下的绝对路径- 循环取出
test文件夹中的.yo文件并逐个拷贝到ROM.yo文件中 - 使用
ROMgen.py读取ROM.yo中的内容,裁剪其中的十六进制汇编指令后生成ROM.txt文件 - 执行
iverilog仿真,并将仿真结果写入到Y86-output.txt文件中 - 使用
Y86-output-yml.py逐行将Y86-output.txt中的CPU运行状态转换为Yaml格式的Y86-output.yml文件 - 将
Y86-output.yml文件重命名后放入Y86-output文件夹,并开始下一轮循环
- 循环取出
循环结束后使用
Y86-output-check.py逐个比较文件夹Y86-output和Y86-answer中的每个文件,如果完全匹配则输出All tests passed!,否则输出Test failed!
1 | #!/usr/bin/python3 |
脚本自动化的具体实现
ROMpath.py
由于IVerilog对于$readmemh()只支持文件的绝对路径,
导致每次移植时都需要手动修改InstMemory.v和Mem.v中的ROM.txt路径
所以编写了这个Python脚本ROMpath.py,用于自动修改InstMemory.v和Mem.v中的ROM.txt路径为当前目录下的绝对路径
1 | #!/usr/bin/python3 |
ROMgen.py
由于Y86-64的指令长度不固定,所以需要对ROM.yo文件中的指令进行裁剪,只保留指令部分,然后将这些十六进制指令按照每行一个字节的格式写入ROM.txt文件中
1 | #!/usr/bin/python3 |
Y86-output-yml.py
由于Verilog的$monitor()和$display输出格式有限,不方便直接输出Yaml格式
所以编写了这个Python脚本Y86-output-yml.py,用于将Y86-output.txt中的内存状态和CPU运行状态转换为Yaml格式的Y86-output.yml文件
1 | #!/usr/bin/python3 |
Y86-output-check.py
使用Python脚本Y86-output-check.py逐个比较文件夹Y86-output和Y86-answer中的每个文件,如果完全匹配则输出All tests passed!,否则输出Test failed!
1 | #!/usr/bin/python3 |
使用Bash脚本快速调试仿真单个Y86程序
运行代码前请先配置好WSL和IVerilog环境
由于每次调试单个Y86程序都需要手动执行一系列命令,所以编写了这个Bash脚本zcmd.sh
方便快速调试Verilog仿真单个Y86程序
1 | rm -f ROM.txt ROM_M.txt Y86-output.txt Y86-output.yml |